Skeletal muscles
The skeleton Joints
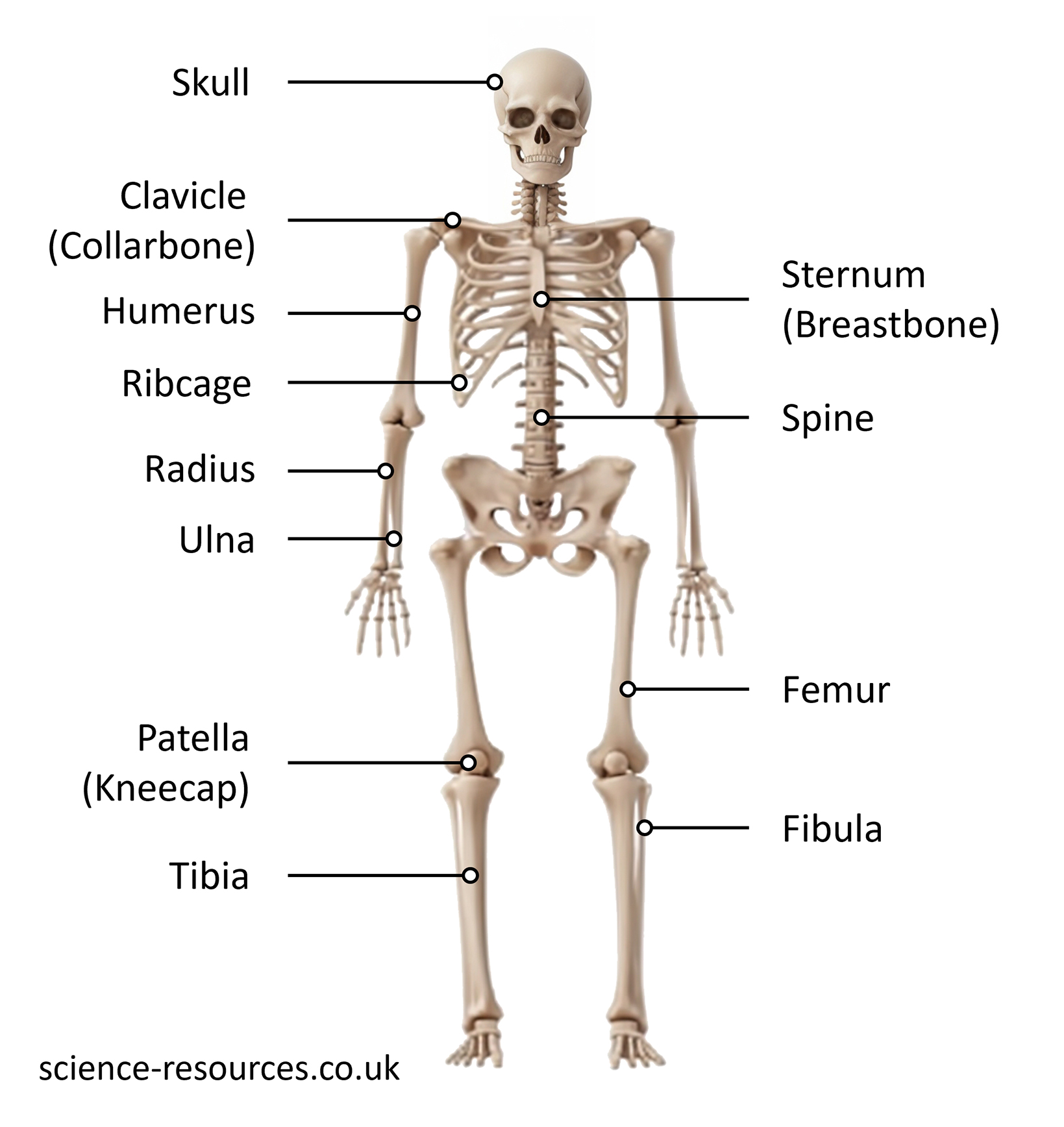
The skeleton is made up of more than 200 bones. It has four main functions:
Joints are where bones move in different directions, like elbows and knees. Muscles pull bones at joints, but they are not directly connected. Bones have ligaments, which are strong cords that attach them to each other. Muscles have tendons, which are also strong cords that attach them to bones. Muscles contract and relax to move bones at joints.
Muscles Antagonistic pairs
Muscles are bundles of cells that form muscle tissue. There are three kinds of muscle cells: cardiac, smooth, and skeletal. Cardiac cells pump blood in our bodies. Smooth cells make thin muscles, like in the stomach. Skeletal cells join bones and move them at joints. Muscles can only contract and relax. Skeletal muscles can only pull bones, not push them. So they work in pairs, called antagonistic muscles, to move joints back and forth.
Muscles work together in pairs at a joint to allow movement, called antagonistic pairs. One muscle in the pair contracts while the other relaxes. For example, at the elbow joint:
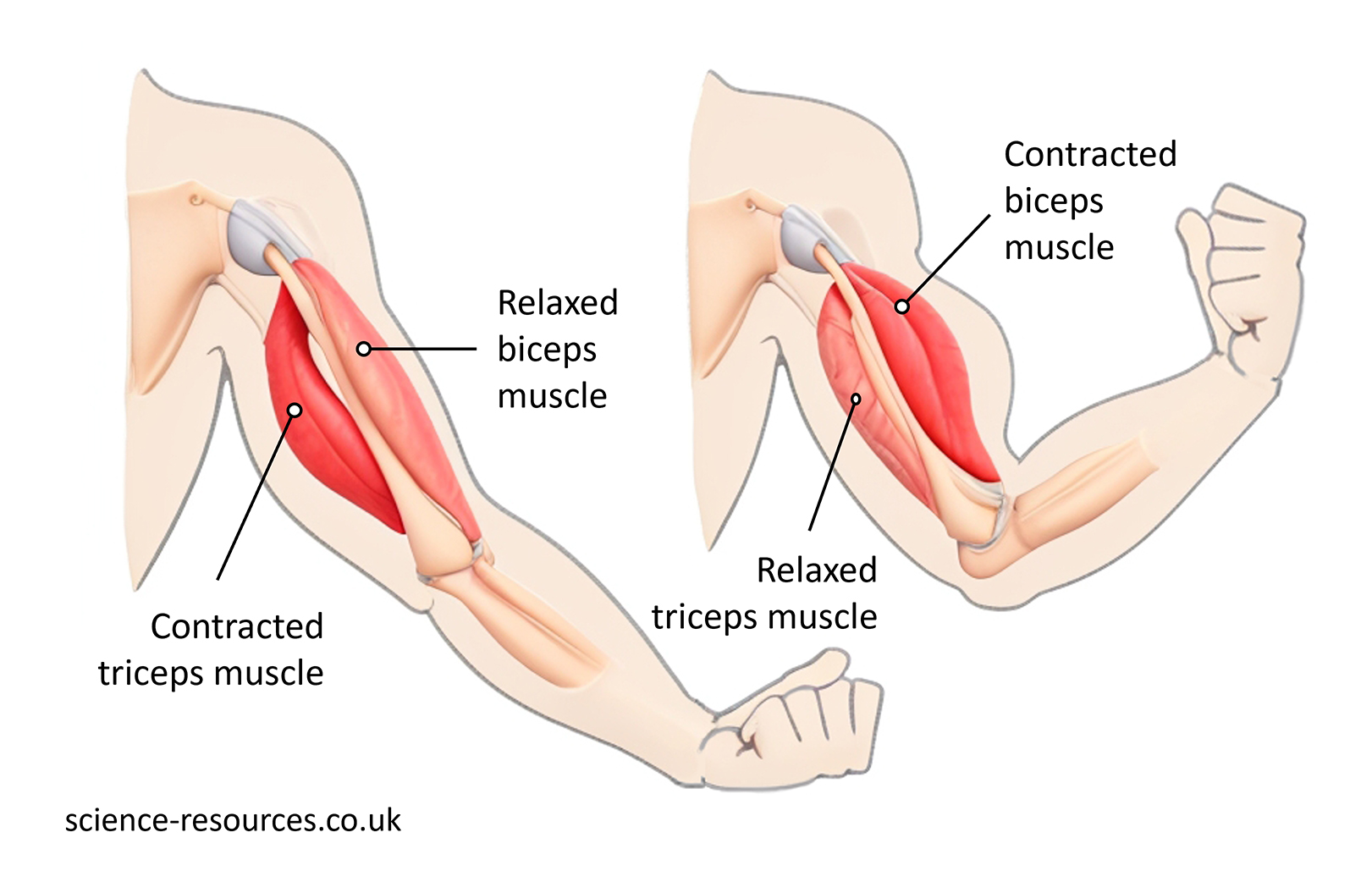
Summary: